Complexity of Algorithms
Quantum Algorithms:
Designing Quantum Algorithms:
- Understand the problem, the input and output requirements.
- Convert the inputs and outputs to quantum states
- Design an efficient circuit which would convert the input quantum state to output quantum state.
Measuring effectiveness of algorithm:
- Accuracy: Determines how close is the estimated output is to the desired output. QA is highly probabilistic and hence is suitable for probabilistic, heuristic and approximate problems.
- Efficiency: The quickness of the algorithm to solve the problem with less resource. This is often measured using Big-O notations.
Big O notation
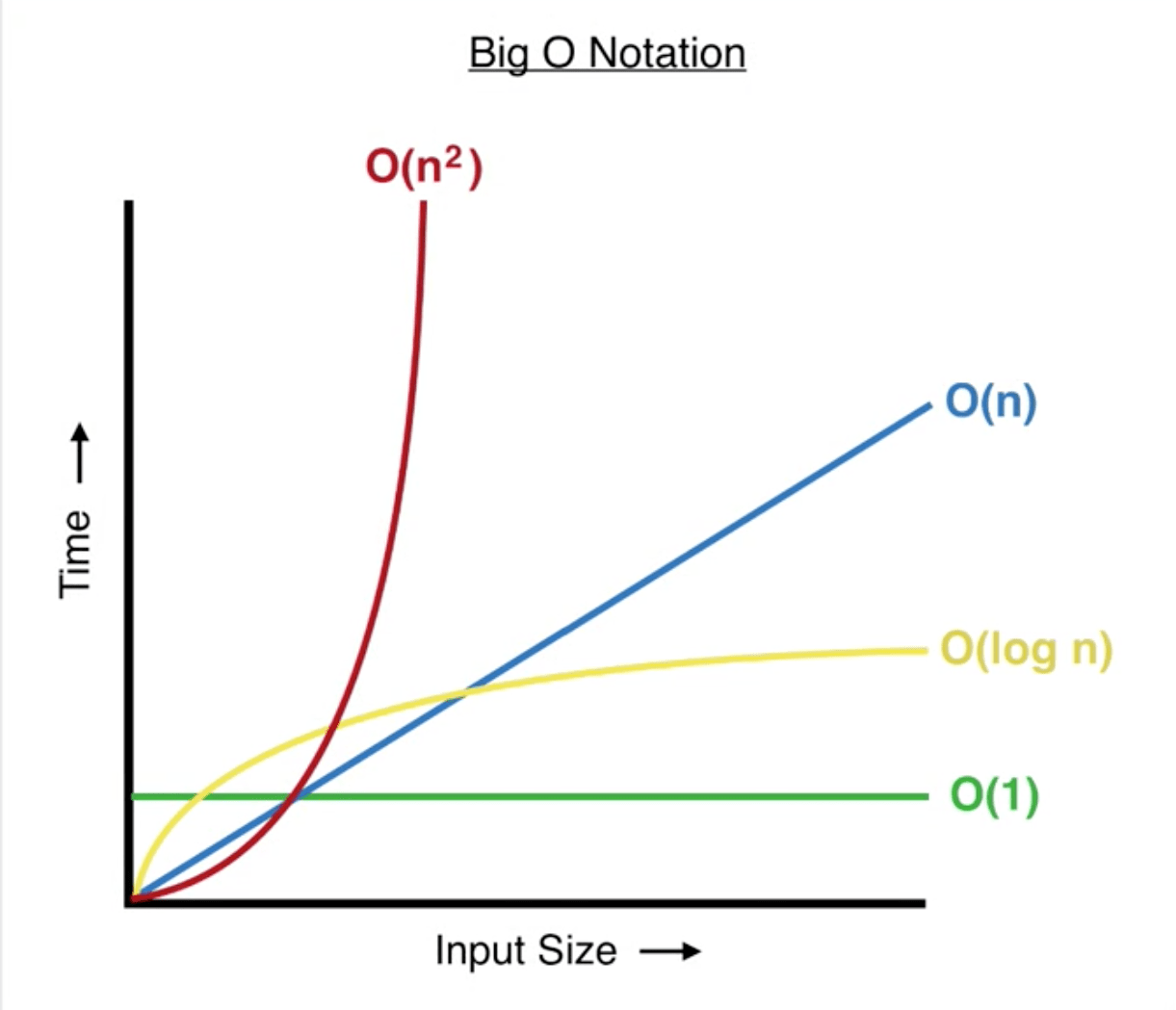
Note: While calculating Big-O we:
- Set all constants to 1 (.i.e we ignore them)
- Keep the highest power alone
P and NP problems:
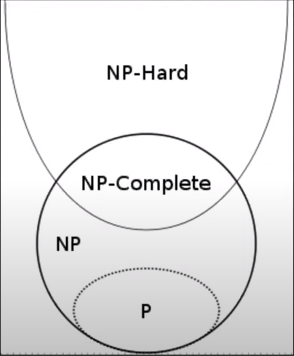
- P-problems can be solved efficiently with polynomial Big-O.
- NP-problems can be checked efficiently with polynomial Big-O.
- NP-hard: One of the most difficult problems
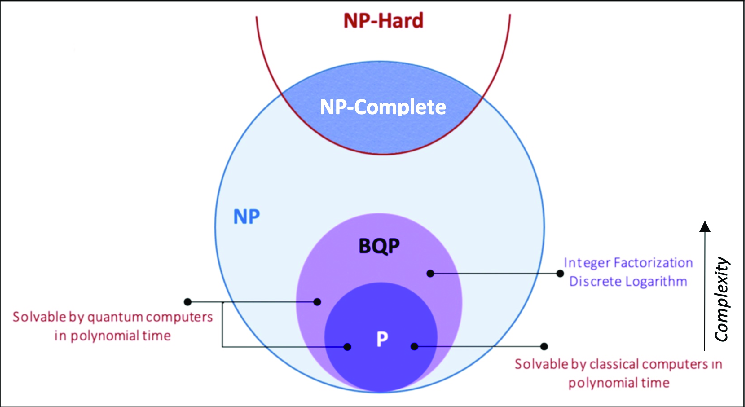
Quantum complexity theory states that some problems of NP can be solved which are called as BQP problems.
Quantum Oracle
An oracle is a part of an algorithm that can perform specific computation for free. The trade-off is that we cannot know how they do it. The approach of Oracle is called as ‘black-box’ but they always return accurate output.
In case of quantum oracle, it takes Quantum states as inputs and gives output as a quantum state. Quantum Oracle can be implemented using Quantum circuit.